What is Mutual Fund Investment? A Comprehensive Guide
In today’s fast-paced financial world, where saving and growing your money is essential, mutual funds have emerged as a popular and accessible investment option. If you’ve ever asked yourself, “What is Mutual Fund Investment?” or wondered how to make the most of your money in a structured and risk-managed way, this guide will give you a detailed understanding. We will explore what is mutual fund investment entails, how they work, the different types, and the pros and cons associated with them, especially in modern investment strategies.
What is a Mutual Fund?
A mutual fund is a pool of money collected from multiple investors to invest in a diversified portfolio of assets such as stocks, bonds, or other securities. These funds are managed by professional fund managers who strategically allocate the pooled resources to maximize returns. Mutual funds allow small investors to access a diversified portfolio without needing significant capital or expertise. In simple terms, a mutual fund is an efficient way to spread your investment across different financial instruments, minimizing risks while aiming for growth.
Also Read the Article: Curious about Toluna Survey Review? This guide breaks down how Toluna works, how you can earn rewards, and whether it’s a legitimate way to make money online.

Importance of Mutual Funds in Modern Investment
In the context of personal financial planning, what is mutual fund investment? Mutual funds have become a key player due to their ability to offer professional management, diversification, and flexibility. With the increasing complexity of markets, individual investors often lack the time and expertise to manage their own investments. What is mutual fund investment? It provides a structured solution by offering a range of investment options suited to different risk profiles and financial goals. Mutual funds play an essential role in long-term wealth creation and retirement planning, making them a cornerstone in modern financial strategies.
How Does a Mutual Fund Work?
Pooling of Money
Mutual funds operate by collecting money from various investors. This pooled capital is then invested in various financial markets, including stocks, bonds, and money markets. By pooling resources, investors gain access to a larger, diversified portfolio that would otherwise be difficult to create individually. The pooling of money helps spread out the risk while maximizing the chances of higher returns.
Role of a Fund Manager
A professional fund manager plays a pivotal role in managing the mutual fund. The fund manager is responsible for researching markets, selecting investments, and making informed decisions on where to allocate the funds. Their expertise and market analysis drive the fund’s performance, making it crucial to choose a fund managed by experienced professionals. The fund manager’s main goal is to optimize returns while minimizing risks in line with the fund’s objectives.

Investment in Different Assets
Mutual funds diversify investments across various asset classes, including equities (stocks), fixed-income securities (bonds), and money market instruments. This diversification helps spread the risk of investment, ensuring that the performance of one asset class does not drastically impact the overall portfolio. For instance, if the stock market performs poorly, the bonds or other safer assets may balance out the loss, providing stability to the portfolio.
Also Read the Article: Looking to make money from home? This article highlights the top skills you can learn to boost your income without leaving the comfort of your home.
Types of Mutual Funds
Mutual funds come in various forms, each designed to cater to the diverse financial goals, risk tolerance, and investment horizons of different investors. Below are the key types of mutual funds that investors can choose from:
1. Equity Mutual Funds
Equity mutual funds primarily invest in stocks and shares of companies. These funds are focused on long-term capital appreciation and are ideal for investors who are looking for growth. However, equity mutual funds come with a higher level of risk due to the volatility of the stock market.
Key Features of Equity Mutual Funds:
Example: An investor who is young and can tolerate high market volatility may opt for an equity mutual fund to grow their wealth over time.
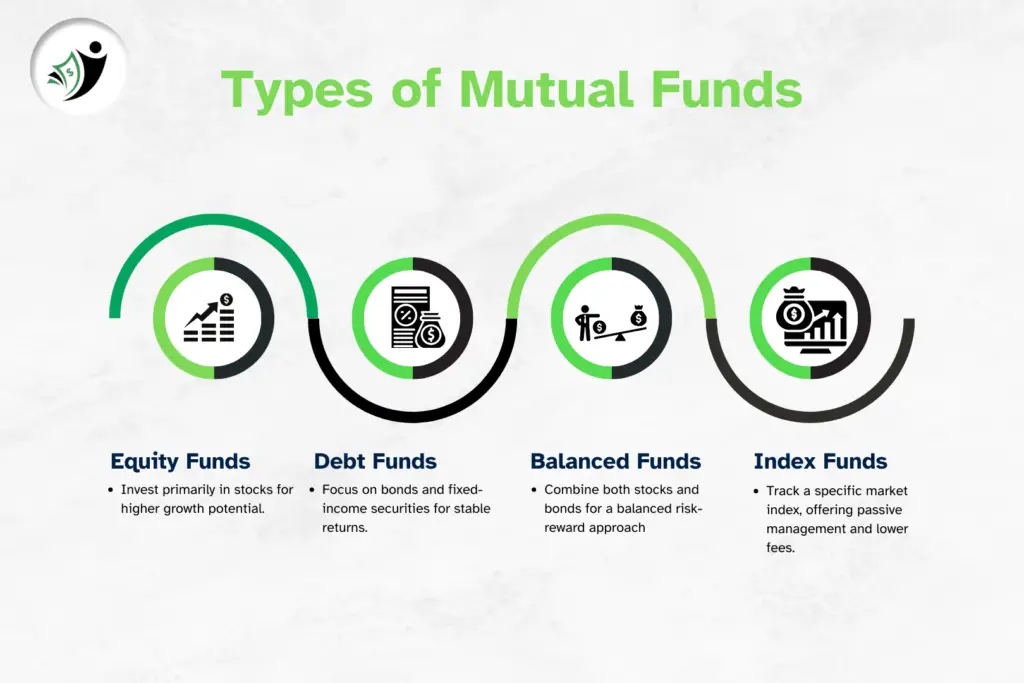
2. Debt Mutual Funds
Debt mutual funds invest in fixed-income securities such as government bonds, corporate bonds, treasury bills, and debentures. These funds are typically less volatile compared to equity mutual funds and provide more stable and consistent returns.
Key Features of Debt Mutual Funds:
Example: An investor who is risk-averse and prefers stable returns might choose debt mutual funds as a safer investment option.

3. Balanced or Hybrid Funds
Balanced or hybrid mutual funds offer a blend of both equity and debt investments. The idea behind these funds is to provide a balanced approach to investing, where investors can enjoy the growth potential of equity investments while also benefiting from the stability of debt investments.
Key Features of Balanced or Hybrid Funds:
Example: A middle-aged investor who seeks both growth and stability might opt for a balanced fund to enjoy the best of both worlds.
4. Index Funds
Index funds are passively managed mutual funds that replicate the performance of a specific market index, such as the Nifty 50 or the S&P 500. Instead of actively choosing stocks, these funds simply invest in all the securities that make up the index, in the same proportion.

Key Features of Index Funds:
Example: An investor who wants a low-cost, diversified exposure to the stock market without actively managing their investments would find index funds appealing.
Benefits of Mutual Fund Investment
1. Diversification
One of the key benefits of investing in mutual funds is diversification. By investing in multiple assets, mutual funds help reduce the risk associated with investing in just one stock or bond. A diversified portfolio is less likely to suffer a significant loss compared to investing in a single asset.
2. Professional Management
Mutual funds offer the advantage of professional management. Fund managers use their expertise and resources to make informed investment decisions, which can lead to better returns than what an individual investor might achieve on their own.
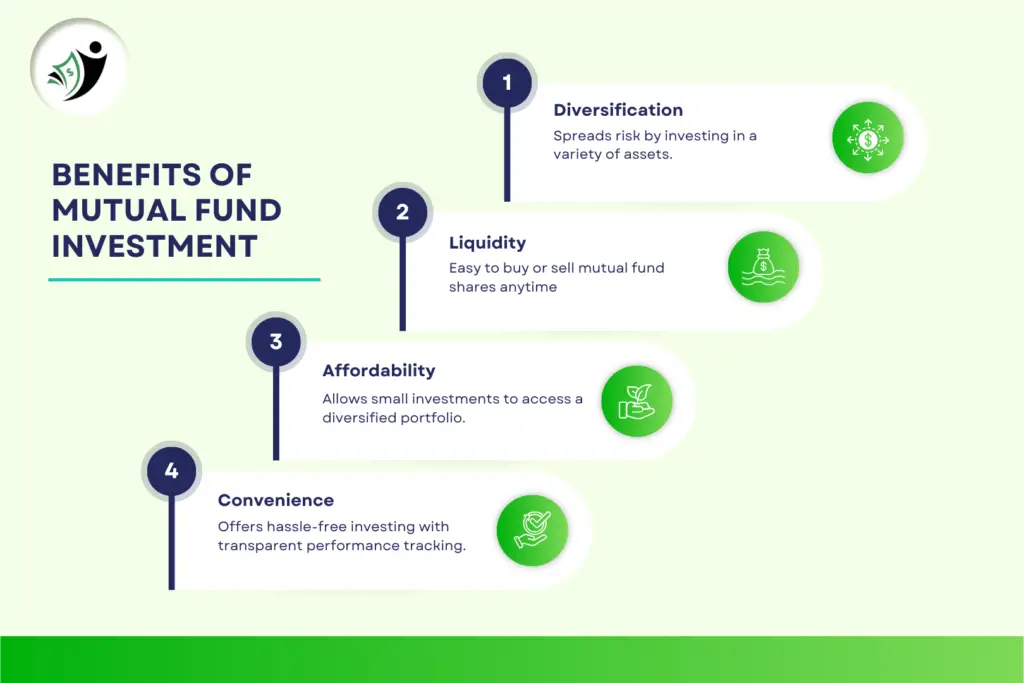
3. Liquidity
Mutual funds offer high liquidity, meaning you can easily buy or sell your mutual fund units. This provides flexibility to investors, allowing them to exit the investment when needed, without being locked in for an extended period.
4. Cost Efficiency
Mutual funds often offer cost benefits due to economies of scale. Since mutual funds aggregate a large amount of money, the transaction costs per investor are lower compared to individual investments in stocks or bonds.
5. Accessibility
Mutual funds are accessible to investors of all sizes. Whether you want to start small with a systematic investment plan (SIP) or make a larger lump sum investment, mutual funds cater to every investor’s needs.
Risks Associated with Mutual Fund Investment
1. Market Risk
All investments in mutual funds are subject to market risks. Equity mutual funds, in particular, can be volatile due to market fluctuations. A downturn in the market can reduce the value of your investment. It’s essential to assess your risk tolerance before investing.
2. Credit Risk
For debt mutual funds, credit risk arises when the issuer of a bond fails to repay the interest or principal. This can result in losses for the mutual fund and its investors. Investors in debt mutual funds should consider the creditworthiness of the bonds in which the fund invests.
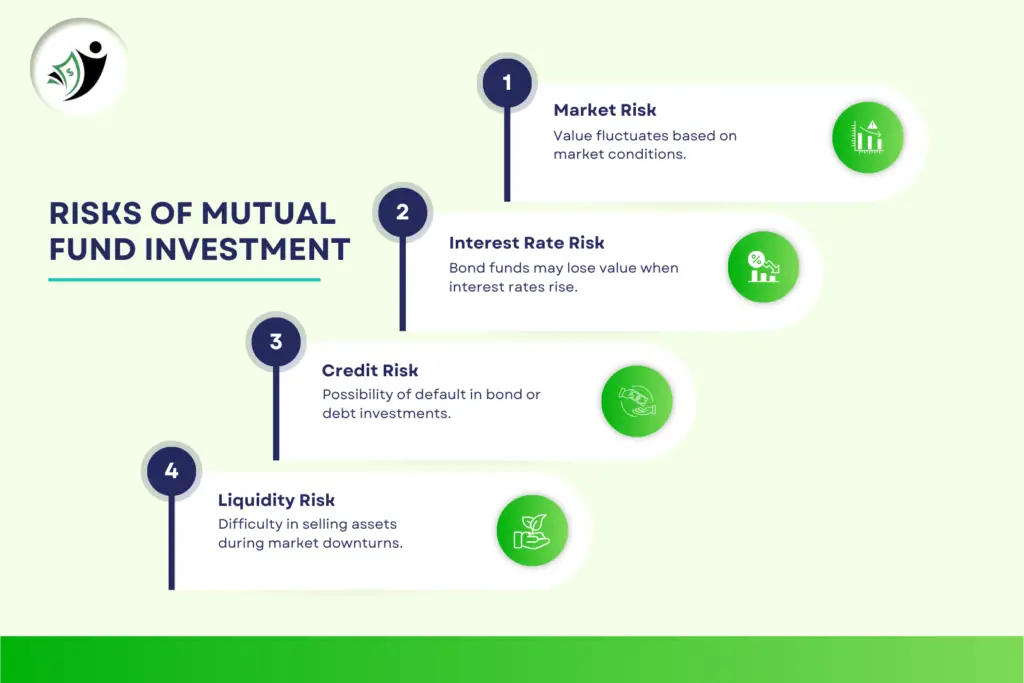
3. Interest Rate Risk
Interest rate changes can significantly impact debt mutual funds. When interest rates rise, bond prices tend to fall, affecting the value of debt mutual funds. This is known as interest rate risk and is crucial for investors to consider when investing in bonds or bond funds.
4. Inflation Risk
Inflation can erode the purchasing power of your returns. If the returns from your mutual fund investment do not outpace inflation, you may end up with less real wealth than anticipated.
How to Invest in Mutual Funds?

Taxation on Mutual Funds

Common Myths about Mutual Fund Investment
Myth 1: What is Mutual Fund Investment Only for Experts?
A common belief is that what is mutual fund investment is too complicated for the average investor and is only meant for financial experts. This myth often prevents beginners from considering what is mutual fund investment as a viable option. However, what is mutual fund investment is specifically designed to cater to all types of investors, from novices to experienced ones. Professional fund managers handle all critical decisions, making what is mutual fund investment accessible even to those without in-depth financial knowledge.
Thus, the idea that what is mutual fund investment is only for experts is a misconception. What is mutual fund investment is one of the most accessible and versatile options for beginners.
Myth 2: What is Mutual Fund Investment Risky?
Another misconception is that what is mutual fund investment is extremely risky. While what is mutual fund investment involves some level of risk, not all funds are high-risk. For instance, equity mutual funds, which are a part of what is mutual fund investment, are riskier but offer potential long-term gains. On the other hand, debt mutual funds are much less volatile, making them suitable for risk-averse investors. What is mutual fund investment also involves diversification, which spreads the risk across assets, reducing potential losses.
In conclusion, what is mutual fund investment is not inherently risky. With the right selection, you can manage and reduce risks effectively.
Myth 3: High Returns are Guaranteed with What is Mutual Fund Investment
Some mistakenly believe that what is mutual fund investment always delivers high returns. The reality is that what is mutual fund investment is market-linked, and returns vary based on market conditions. While equity mutual funds may offer high returns during a booming market, they may underperform during a downturn. Debt funds, mutual fund investments, are also influenced by factors like interest rates.
In short, what is mutual fund investment can provide attractive returns, but it is not a guarantee of high returns at all times.
Myth 4: What is Mutual Fund Investment Expensive?
Some people think that investing in mutual funds requires a large sum of money, which keeps them from considering it as an option. However, this is far from the truth. One of the greatest advantages of mutual funds is their accessibility to all types of investors, including those with small budgets.
Most mutual funds allow you to start investing with as little as ₹500 through Systematic Investment Plans (SIPs). SIPs enable you to invest a fixed amount at regular intervals, making it affordable for even those with limited financial resources. In addition, mutual funds offer lower transaction costs when compared to directly investing in individual stocks or bonds, which makes them cost-effective for retail investors.
Therefore, mutual funds are an affordable investment option that allows you to start small and gradually build your wealth over time.

Myth 5: What is Mutual Fund Investment Locks Your Money for Years
Another myth is that once you invest in a mutual fund, your money is locked for years, making it inaccessible in case of emergencies. While it’s true that some mutual funds have a lock-in period, such as tax-saving mutual funds (ELSS), most mutual funds provide liquidity, allowing you to redeem your investment at any time.
Open-ended mutual funds, for instance, have no lock-in period, and you can easily buy or sell your units on any business day. The ease of liquidity is one of the key benefits of mutual funds, making them a flexible investment option.
In summary, most mutual funds offer easy access to your money, contrary to the belief that your investment is locked in for years.
Myth 6: You Need to Constantly Monitor What is Mutual Fund Investment
Many people are under the impression that mutual fund investments require constant monitoring and regular buying or selling, which can be stressful for those with busy schedules. While keeping an eye on your investments is always a good practice, mutual funds don’t require day-to-day management from individual investors.
Professional fund managers take care of managing the fund and making necessary adjustments to the portfolio. By investing in a well-chosen mutual fund that aligns with your financial goals, you can rest easy knowing that your money is in expert hands.

Myth 7: Past Performance Guarantees Future Results in What is Mutual Fund Investment
One of the most common myths is that if a mutual fund has performed well in the past, it will continue to do so in the future. While past performance can give you some insights into the fund’s management and consistency, it is not a reliable predictor of future performance. Market conditions change, and various factors can impact the fund’s future performance.
Investors should avoid relying solely on past performance and instead focus on the fund’s overall investment strategy, the quality of its management team, and whether it aligns with their long-term financial goals.
Myth 8: What is Mutual Fund Investment Only Benefits Long-Term Investors
While mutual funds are ideal for long-term wealth creation, there are short-term mutual funds as well that cater to investors with a shorter investment horizon. For example, liquid mutual funds and ultra-short-term funds are designed for short-term goals, offering stable returns with low risk. These funds invest in highly liquid assets, making them suitable for investors seeking returns over a short period.
Myth 9: What is Mutual Fund Investment Not Transparent
Many believe that mutual funds lack transparency and that investors don’t have sufficient information about where their money is being invested. In reality, mutual funds are one of the most transparent investment options. Fund houses are required to provide regular updates about their portfolio holdings, NAV (Net Asset Value), and performance reports. Investors receive periodic statements, and most of this information is also available online, making it easy to track.
Myth 10: You Need to Time the Market for What is Mutual Fund Investment
Another myth is that you need to time the market for what is mutual fund investment. However, regular investment through SIPs helps average out costs and eliminates the need for market timing in what is mutual fund investment.
FAQs on What is Mutual Fund Investment
What is a mutual fund investment?
A mutual fund investment involves pooling money from multiple investors to purchase a diversified portfolio of stocks, bonds, or other securities. The fund is managed by a professional fund manager who invests the money on behalf of the investors to achieve specific financial goals.
How does a mutual fund work?
Mutual funds work by collecting money from a large number of investors. This pooled money is then invested in a variety of assets such as equities, bonds, or money market instruments. The returns are distributed proportionately among the investors based on their contribution to the fund.
What are the types of mutual funds available?
Mutual funds can be broadly categorized into equity funds (investing in stocks), debt funds (investing in bonds), balanced or hybrid funds (a mix of stocks and bonds), and index funds (which track a specific market index like Nifty or S&P 500).
What is the difference between equity and debt mutual funds?
Equity mutual funds invest primarily in stocks and are suitable for investors looking for long-term growth but with higher risk. Debt mutual funds, on the other hand, invest in bonds and fixed-income securities, offering lower risk with stable returns.
What are the benefits of investing in mutual funds?
The main benefits include diversification (spread risk across assets), professional management (handled by experts), liquidity (easy to buy or sell units), accessibility (suitable for all types of investors), and cost-efficiency (lower transaction costs compared to direct investments).
Is mutual fund investment risky?
Yes, mutual funds carry some level of risk, as their performance is linked to market movements. However, the level of risk depends on the type of mutual fund chosen. For example, equity funds have higher risk compared to debt funds. Investors should align their choice with their risk tolerance.
What is a Systematic Investment Plan (SIP)?
SIP is a method of investing in mutual funds where an investor commits to investing a fixed amount at regular intervals (monthly or quarterly). This helps in averaging out the investment cost and is ideal for long-term wealth building.
How are mutual funds taxed?
The taxation on mutual funds depends on the type of fund and the duration for which the investment is held. For equity mutual funds, long-term capital gains (held for over a year) are taxed at 10%, while short-term capital gains are taxed at 15%. Debt mutual funds have different tax implications, with long-term gains taxed at 20% with indexation benefits.
Can I lose money in mutual funds?
Yes, there is a risk of losing money in mutual funds due to market fluctuations, especially with equity funds. However, with a well-diversified portfolio and professional fund management, the risk can be mitigated over time.
How do I choose the right mutual fund?
To choose the right mutual fund, consider your financial goals, risk tolerance, investment horizon, and the fund’s past performance. It’s also crucial to review the fund’s expense ratio and the credibility of the fund manager before investing
Conclusion Of What is Mutual Fund Investment
Mutual funds offer a flexible and effective way to grow your wealth through diversification, professional management, and a variety of investment options. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced investor, mutual funds can help you achieve your financial goals. By understanding the basics of what is mutual fund investment, you can make informed decisions that align with your long-term financial strategies.




